Chapter 4 Managing Wireless Network
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Wireless
Wireless
In Wireless, you can configure the SSID(Wi-Fi name), Encryption Method, Password, and other wireless parameters for both the 2.4G and 5G networks.
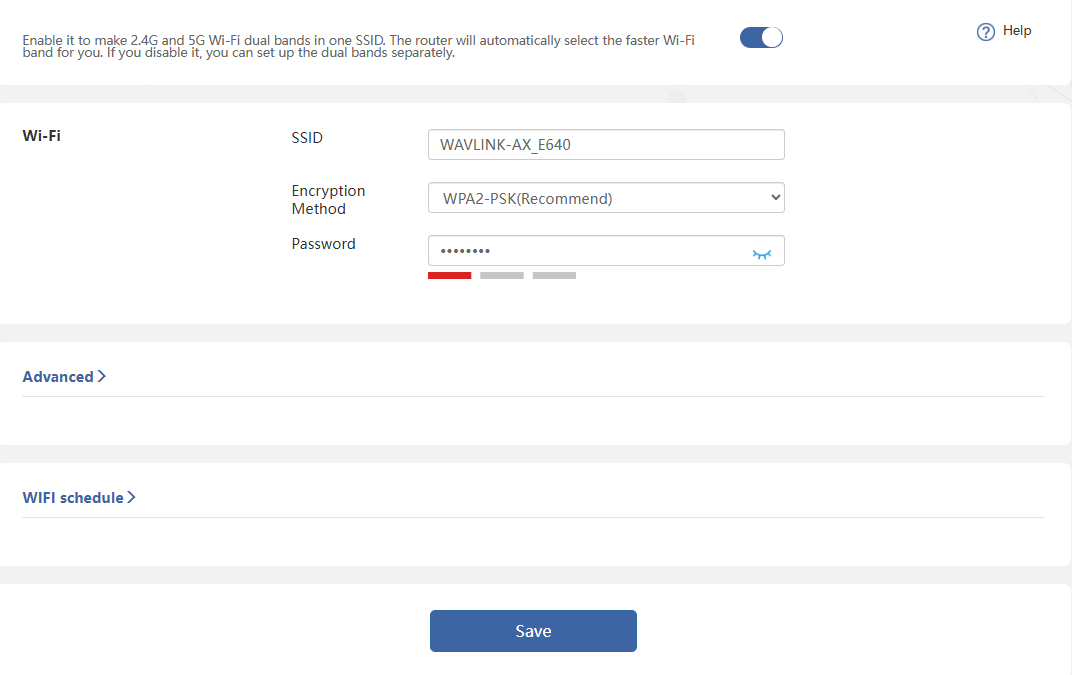
Band Steering
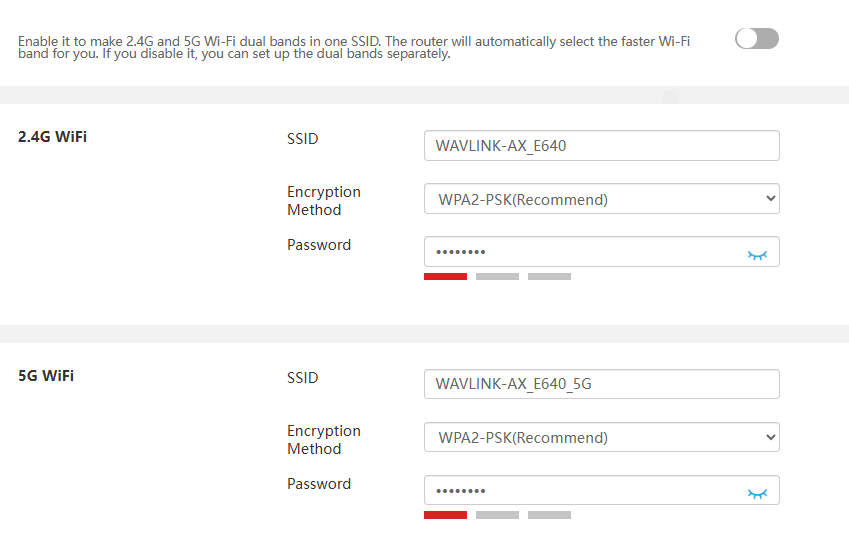
When enabled Band Steering, both 2.4GHz and 5GHz wireless networks share the same Wi-Fi name. The router will dynamically assign devices to the optimal frequency band based on real-time network conditions. When disabled, you may configure separate Wi-Fi names and settings for the 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands.
SSID(Wi-Fi Name) and Password
-
Create a new Wi-Fi name in the SSID input field.
-
Select the Encryption Method from the dropdown list(WPA3-SAE/WPA2-PSK is recommended.)
-
Create a new Wi-Fi password in Password.
Note: Using the new password to reconnect to the Wi-Fi network after setting up a new network.
Advanced
- Click Wireless > Advanced.
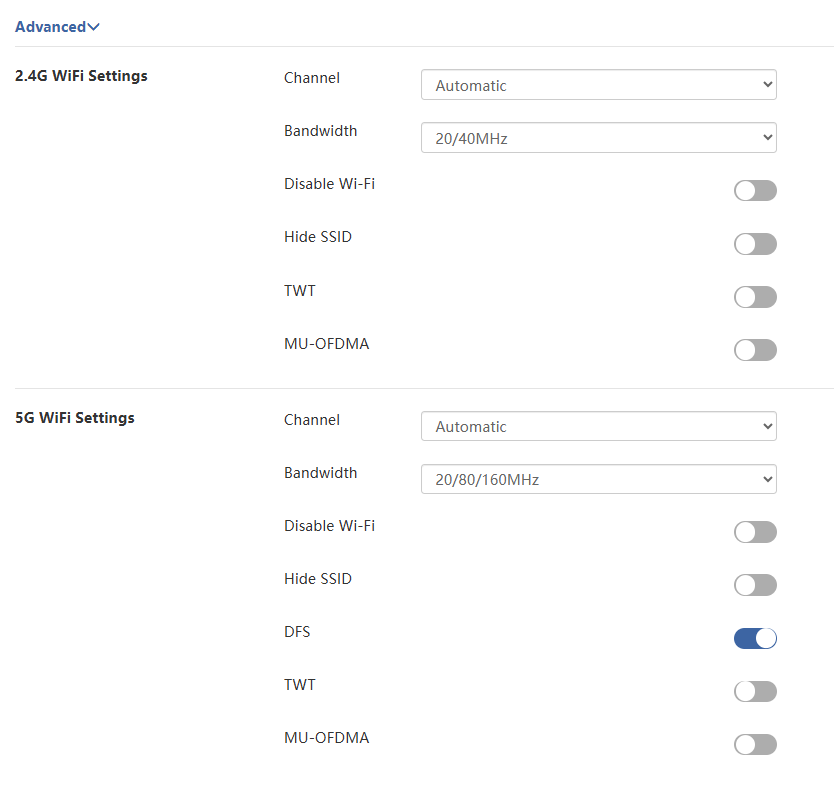
- Channel and Bandwidth:
-
From the Channel dropdown list, select the operating channel for your wireless network. (If you are unsure about which channel to choose, it is recommended to select Automatic, so the device can automatically select the optimal channel based on the surrounding environment for your better network experience.)
-
From the Bandwidth dropdown list, select the bandwidth for the router's wireless data transmission.
- Disable Wi-Fi:
- If enabling this feature, the corresponding Wi-Fi signal will be closed.
- Hide SSID:
- After enabling this, the wireless signal for the corresponding network will be hidden.
- DFS:
- After enabling this, the device will automatically avoid channels that are restricted in your region.
- TWT:
- After enabling this feature, the router will automatically optimize resource scheduling between devices, negotiate target wake time to reduce contention, increase device sleep time, and ultimately extend the lifespan of the router.
Note: TWT compatibility issues may occur with certain terminal devices.
- MU-OFDMA
- Once enabled, the router will implement multi-user channel resource sharing, enhancing transmission efficiency in multi-device environments and reducing network latency.
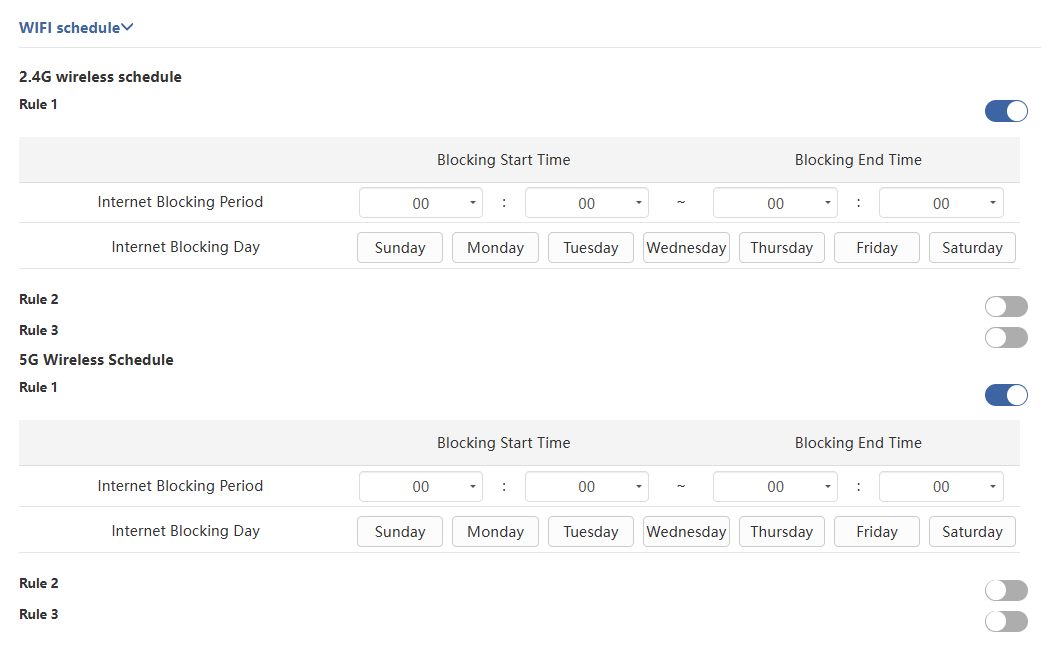
WiFi Schedule (Wireless Timer Switch)
The schedule function allows you to customize the date and time to control the wireless network switch, with up to three rules definable for the 2.4G and 5G separately. This feature only takes effect after obtaining the network time and only affects the main network. For the guest network, you need to manually enable or disable this feature or define separate rules within the Guest Network settings.
-
Navigate to Wireless > WiFi Schedule.
-
Click on Rule 1/2/3 under either the 2.4G wireless schedule or 5G Wireless Schedule to set the timing rules.
-
Click Save to complete the settings.
Note:
- The schedule is based on the router's time. You can modify the time in Advanced > Time Zone.
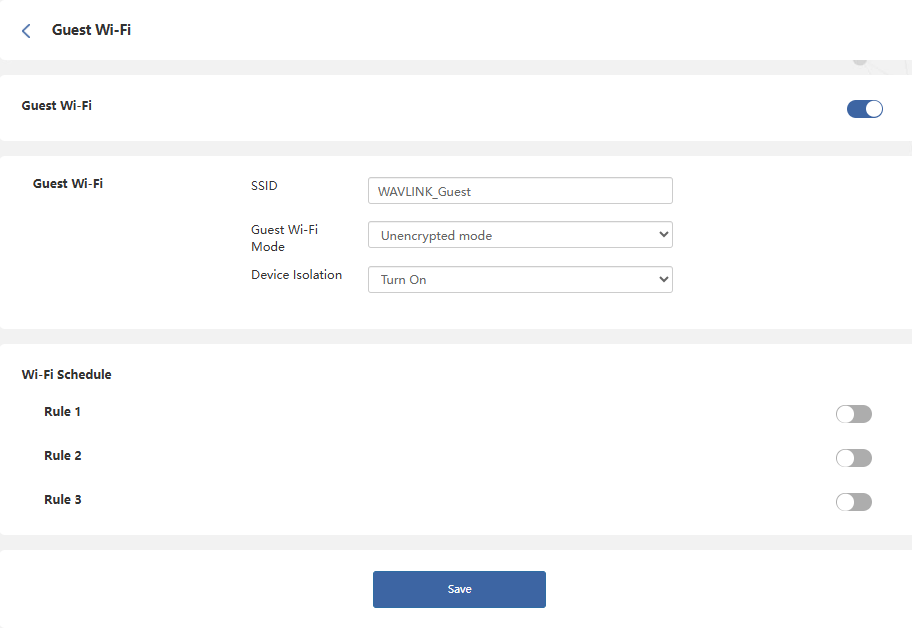
Guest Wi-Fi
This feature allows you to provide Wi-Fi to guests without exposing your main network. When you have visitors at your home, apartment, or workplace, you can create a guest Wi-Fi for them. Additionally, you can customize guest Wi-Fi settings to ensure security and privacy.
-
Navigate to Advanced > Guest Wi-Fi.
-
Click to enable Guest Wi-Fi.
-
Set the SSID(Wi-Fi Name).
-
Set the encryption method in the Guest Wi-Fi Mode, you need create a password if chossing encrypted mode; You do not need a password to access the network if choossing Unencrypted mode.
-
If enable the Device Isolation, the devices will not support mutual access.
-
Set the opening time of guest Wi-Fi in the WIFI schedule.
-
Click Save to complete the settings.
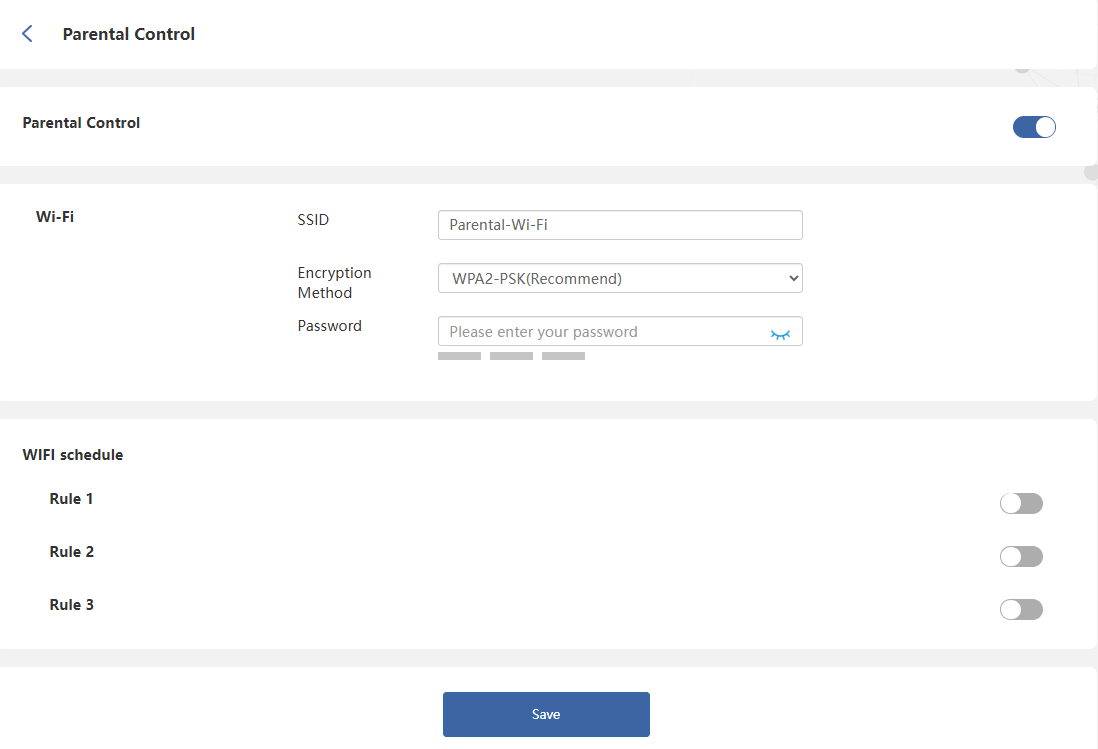
Parental Control
Parental Wi-Fi allows you to set up a separate wireless network for family members. You can configure its SSID, encryption method, and rules.
-
Navigate to Advanced > Parental Control.
-
Click to enable Parental Control.
-
Set the SSID, Encryption Method, and Password.
-
Set the Internet Blocking Period and Internet Blocking Day in Rule 1/2/3 to control internet access time.
-
Click Save to complete the settings.
Signal Adjustment
In environments with different areas, the requirements for the signal transmission strength of routers also vary. Given that signal quality is ensured, larger areas and more obstacles necessitate higher signal strength. In smaller environments, relatively lower signal strength can be configured, which not only saves energy and reduces radiation but also decreases the risk of unauthorized access.
- Click Advanced>Signal Adjustment.
- Select the signal strength from the list of Signal Adjustment.